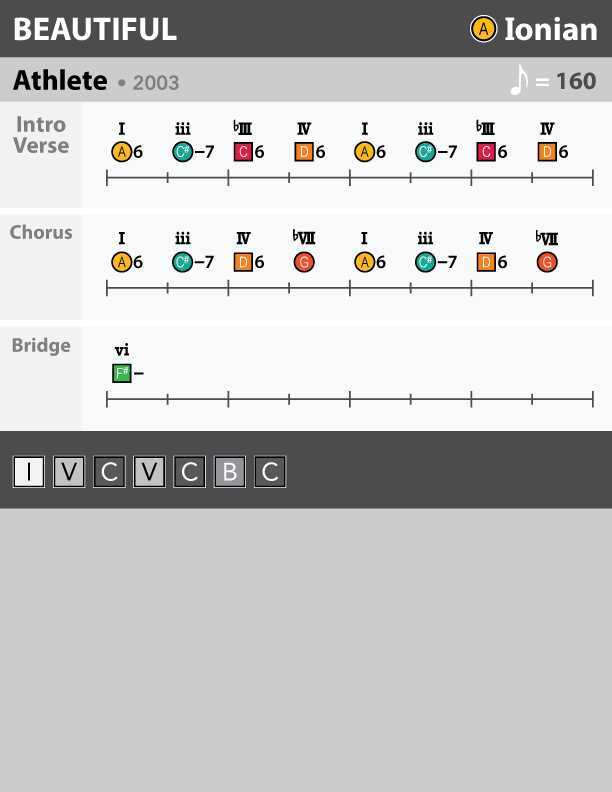
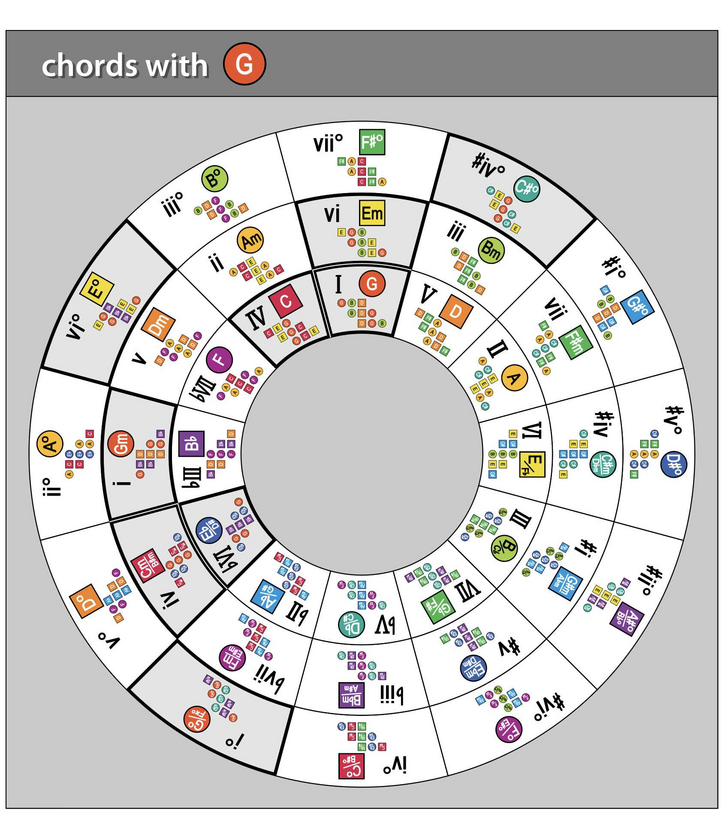
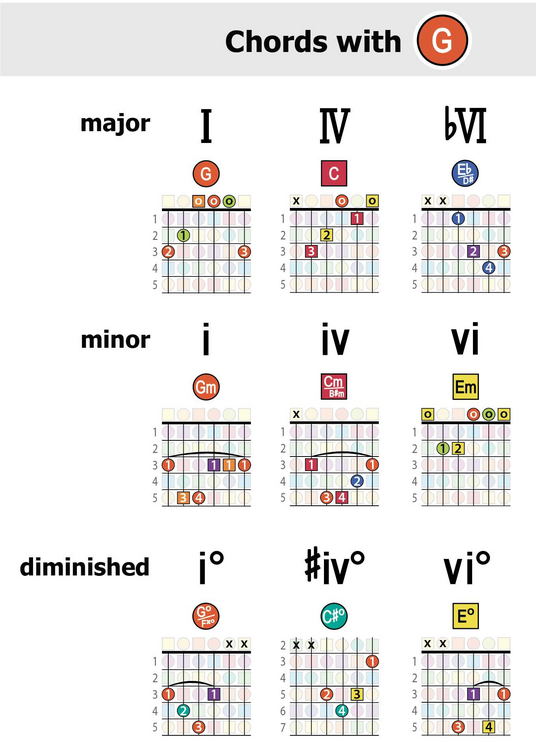
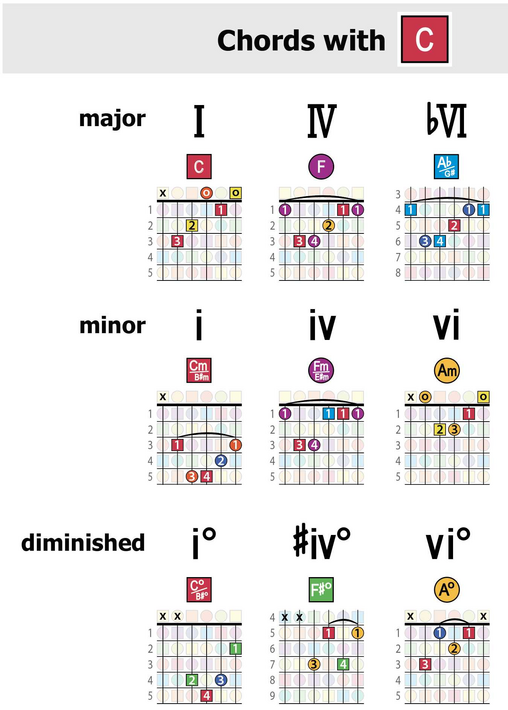
Here's a quick intro to navigating your ChordMap™ -- to crack the code to songwriting. With it, you can identify the key, mode, and chord progressions in a song. Here’s how it works:
Parallel Modes
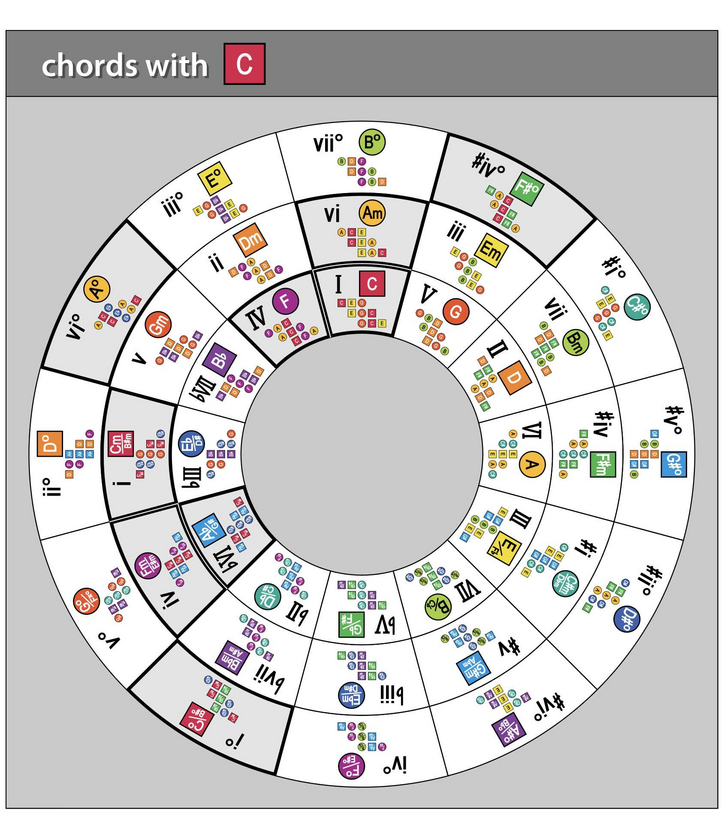
In the circle of fifths, the chords in each key are grouped. Parallel modes (which share the same tonic) are all neighbors in the circle of fifths. These parallel modes are a common source of borrowed chords in songs. Using the key of C, for example:
Rotate the numerals layer to align “I” next to C (the red square in the inner ring). This will also position all of the other numerals with their respective chords.
Holding the numeral layer in place, next rotate the grouping line layer to point at the “Lydian” label. This layer arrangement highlights the chords of C LYDIAN, which includes C major, D major, E minor, F# diminished, G major, A minor, and B minor – marked by numerals I, II, iii, #iv°, V, vi, and vii, respectively:

Continuing to hold the numerals layer in place, you can then rotate the grouping line layer counterclockwise in 30-degree increments. This highlights the other C parallel modes, including C IONIAN (a.k.a. “C major”) with chords C major, D minor, E minor, F major, G major, A minor, and B diminished – marked by numerals, I, ii, iii, IV, V, vi, and vii°:

C MIXOLYDIAN with chords C major, D minor, E diminished, F major, G minor, A minor, and Bb major, marked by numerals I, ii, iii°, IV, v, vi, and bVII, respectively:

C DORIAN with chords chords C minor, D minor, Eb major, F major, G minor, A diminished, and Bb major, marked by numerals i, ii, bIII, IV, v, vi°, and bVII, respectively:

C AEOLIAN (a.k.a. “C minor”) with chords C minor, D diminished, Eb major, F minor, G minor, Ab major, and Bb major, marked by numerals i, ii°, bIII, iv, v, bVI, and bVII, respectively:

C PHRYGIAN with chords C minor, Db major, Eb major, F minor, G diminished, Ab major, and Bb minor, marked by numerals i, bII, bIII, iv, v°, bVI, and bvii, respectively:

And finally, C LOCRIAN with chords C diminished, Db major, Eb minor, F minor, Gb major, Ab major, and Bb minor, marked by numerals i°, bII, biii, iv, bV, bVI, and bvii, respectively:
 Again, by holding the numerals layer in place and rotating the grouping line counterclockwise, you can see each parallel mode – as this image summarizes:
Again, by holding the numerals layer in place and rotating the grouping line counterclockwise, you can see each parallel mode – as this image summarizes:

Relative Modes
The ChordMap also illustrates all relative modes in every key, but moving in reverse. You do this by holding the grouping line layer in place instead and rotating the numerals layer. Using the key of C again, for example:
Rotate the numerals layer to align “I” next to C (the red square in the inner ring). As before, this will position all the other numerals with their respective chords.
Next, position the grouping line layer so that it is pointing directly up to the “Ionian” label. This again highlights the C IONIAN mode (a.k.a. “C major”) with chords C major, D minor, E minor, F major, G major, A minor, and B diminished – marked by numerals, I, ii, iii, IV, V, vi, and vii°:

Holding the grouping line layer in place, rotate the numerals layer 30-degrees in a counterclockwise direction to highlights the chords of F LYDIAN, which includes F major, G major, A minor, B diminished, C major, D minor, and E minor – marked by numerals I, II, iii, #iv°, V, vi, and vii, respectively:

Again keeping the grouping line in place and rotating the numerals 30-degrees clockwise past C Ionian, the G MIXOLYDIAN mode is illustrated, with chords G major, A minor, B diminished, C major, D minor, E minor, and F major – marked by numerals I, ii, iii°, IV, v, vi, and bVII, respectively:

Rotating the numerals further clockwise by 30-degrees, the stationary group line highlights the D DORIAN mode, with D minor, E minor, F major, G major, A minor, B diminished, and C major, marked by numerals i, ii, bIII, IV, v, vi°, and bVII, respectively:

Another clockwise rotation of the numerals by 30-degrees highlights the A AEOLIAN mode, which includes chords A minor, B diminished, C major, D minor, E minor, F major, and G major, marked by numerals i, ii°, bIII, iv, v, bVI, and bVII, respectively:

Yet another 30-degree clockwise rotation of the numerals in relation to the stationary group line highlights E PHRYGIAN, which includes chords E minor, F major, G major, A minor, B diminished, C major, and D minor, marked by numerals i, bII, bIII, iv, v°, bVI, and bvii, respectively:

Finally, one more 30-degree clockwise rotation of the numerals highlights the B LOCRIAN mode, with chords B diminished, C major, D minor, E minor, F major, G major, and A minor, marked by numerals i°, bII, biii, iv, bV, bVI, and bvii, respectively:
 To summarize, these are the seven relative modes of C major:
To summarize, these are the seven relative modes of C major:

Parallel vs. Relative Modes
Because each layer of the ChordMap can move independently, these same relationships are shown in all 12 keys – whether the numerals remain stationary and the grouping line rotates to illustrate PARALLEL modes … or vice versa, with the grouping line made stationary and the numerals rotated in 30-degree increments to highlight RELATIVE modes.
In the examples above, each PARALLEL mode of C is shown to be a permutation of seven other keys:
C Lydian = G Ionian
C Ionian = C Ionian
C Mixolydian = F Ionian
C Dorian = Bb Ionian
C Aeolian = Eb Ionian
C Phrygian = Ab Ionian
C Locrian = Db Ionian
In contrast, each RELATIVE mode C is a permutation of the key of C:
F Lydian = C Ionian
C Ionian = C Ionian
G Mixolydian = C Ionian
D Dorian = C Ionian
A Aeolian = C Ionian
E Phrygian = C Ionian
B Locrian = C Ionian
Again, these relationships are cyclical and symmetrical so you can quickly navigate the circle of fifths. Once you know how to move around the ChordMap, it’s easy to analyze chord progressions, including:
the use of parallel modes for borrowed chords
the use of both parallel and relative modes for modal mixture
the use of modulation (shifting between modes within a composition)
etc.
There’s so much to explore. Enjoy!